Automated Lead Allocation
Automated lead allocation is an Enterprise feature that enables the automated allocation of new leads/enquiries to team members based on different rules you set. Leads can also be automatically reallocated to another user if certain rules are met.
Lead allocation rules
Set if lead allocation is active
When inactive, leads will not be allocated to users. When set to active, allocation will apply to leads added since allocation was turned on. Older leads will not be allocated.
Important: do not turn lead allocation off unless you are happy that after turning it back on, only new leads from the point it was turned on again will be allocated and reallocated (see our FAQs for more details).

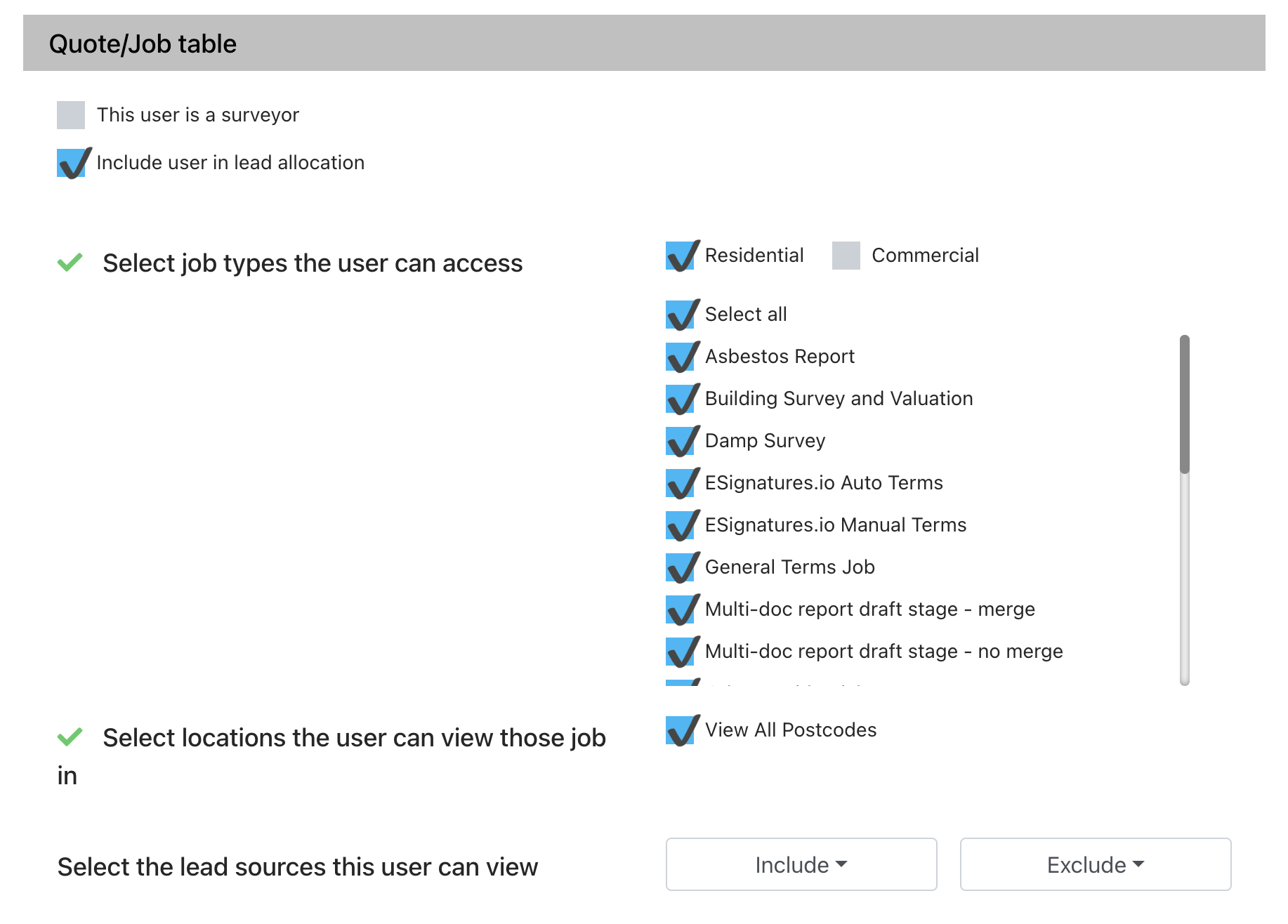
Step 1 - Set which users are included in lead allocation
Click through to the user settings to select which of your users should be included in lead allocation. Only users ticked to be included in lead allocation will be included in the rules below.
- Tick that the user is included in lead allocation
- Set the job types they can be allocated
- Set the locations they can be allocated those job types in
- Set which lead sources the user is allowed to deal with (no selection allows all lead sources). Include allows only specific sources selected, Exclude allows any source apart from the ones selected
View the user settings guide for full details.
Step 2: Set user availability
Set when a user is available for lead allocation and when they are not under Settings > Manage users > User availability settings. A user can only be allocated leads when they are “Available”. You can set a user’s standard working times in the user settings and then import these into the user availability settings page. You can also manually enter working times into the user availability settings.

Step 3: Lead allocation rules
Select allocation method:
- Round robin – the leads are allocated to the next user in the list (who meets all the rules for being allowed to be allocated a lead)
- Lowest lead count – the leads are allocated the user(s) with the lowest lead counts to bring all users up to the same level. Once all users have the same lead count, the leads are allocated in a round robin process
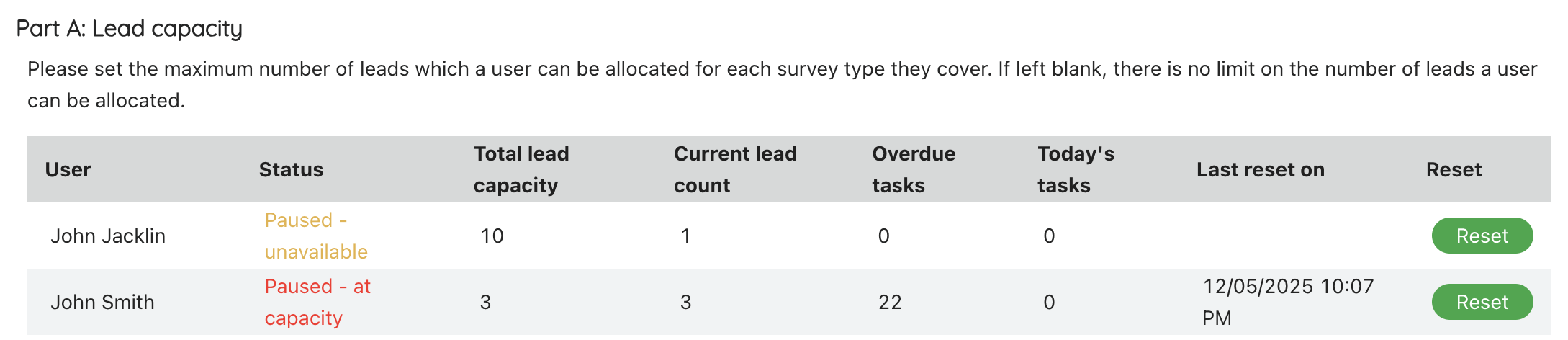
Part A: Lead capacity
Set if users should be capped at the total number of leads they can be allocated before they stop being allowed to receive more leads. You can set lower down in the settings which variables reduce a user’s lead count.
If no value is set, the users are uncapped.
The lead count column shows a user’s current lead count. If needed, you can reset the lead count for each user so that they start from 0 and the lead count starts building up again.
Part B: Availability rules
If you are using our automated lead allocation feature (Enterprise), you can tick this setting so that the system includes this user in the lead allocation process.
Once ticked, set the job types, locations and lead sources that the user deals with. They will then also appear in your lead allocation settings.

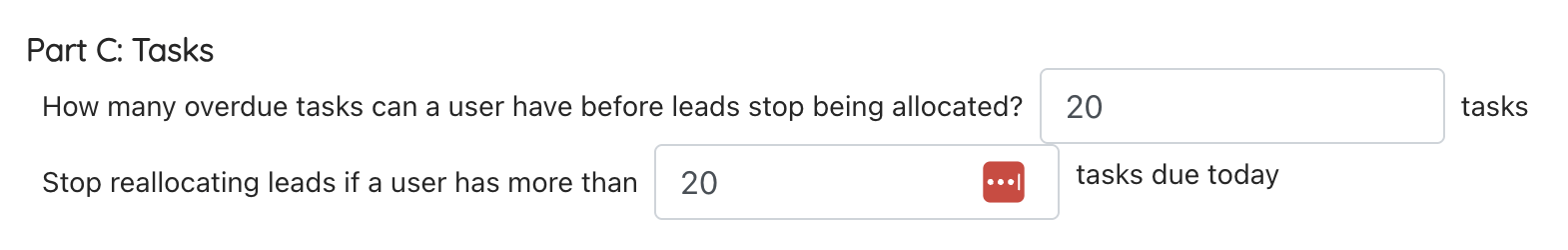
Part C: Tasks
Use this rule to prevent users being allocated more leads if they have too many tasks to be completed:
- Set the number of overdue tasks a user can have before they can no longer receive new leads
- Set the number of tasks due today a user can have before they can no longer receive new leads
Definition: a task counts as overdue if the due date was yesterday or older (we do not include tasks that are past their end time with today’s date). A task due today has a date set for today.
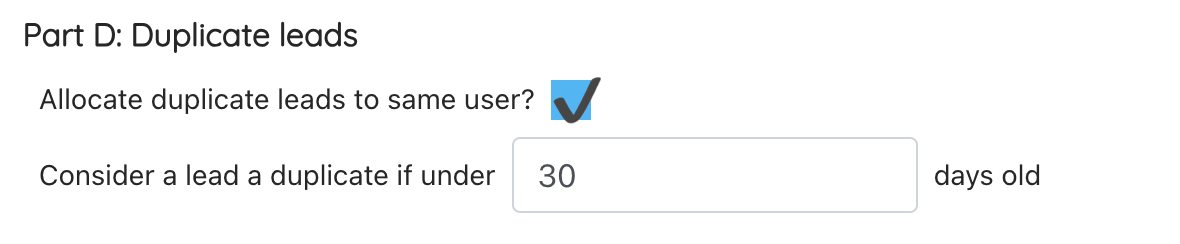
Part D: Duplicate leads
Set if duplicate leads should be allocated to the same user. Duplicates are flagged based on your duplicate lead rules under Settings > Survey settings > Quoting preference > Duplicate fields.
You can also set how old a previous duplicate must be for the new lead to be considered a duplicate for lead allocation. For example, a lead comes in today and is flagged as a duplicate based on your duplicate fields settings, you have set a 30-day window for a lead being a duplicate, if the existing record in the system is over 30 days old, the lead will not be considered a duplicate for lead allocation purposes, but will still show the duplicate flag on the job record. This means the lead could be allocated to any user. If the existing record was under 30 days, the lead would be allocated to the same user that had the first lead.
Lead count: if a lead is a duplicate, the user’s lead count will not increase when this lead is assigned to them. If after checking the lead, they mark the lead as not a duplicate, the user’s lead count will increase by 1 lead. If the user is at capacity, their lead count will show as higher than their lead capacity.
Deleted user: if the original duplicate lead was previously allocated to a user who is now deleted/deactivated the lead is counted as a new lead and can be allocated to any user.
Part E: Manually added leads
This setting controls whether a lead added manually by a user (e.g. added manually during a phone call) is assigned to them by the lead allocation process or if the lead goes into the pot for it to be allocated to any user.
This will take precedence over other rules above – i.e. if a lead is both a duplicate and added manually, the lead will be assigned to the user that added it. All other rules will run where the lead wasn’t added manually by a user.

Part F: Service Level Agreement
This rule sets if a user is allowed to be allocated new leads whilst they still have leads at the SLA stages of Red, Amber and/or Green. If a colour is unticked, users cannot receive new leads whilst they have leads at that status.
Note: this SLA is based on the company SLA. If the user has a lead that has reached the relevant colour for the company, the user will be allowed or not allowed to be allocated leads.

Step 4: Factors that reduce user lead count and stop reallocation
A. Reduce lead count
The rules below can be used to determine which lead status’ reduces a user’s lead count, allowing them to receive more leads if at capacity:
- Lead is archived: If yes, the lead count will reduce when the user marks a lead as archived
- Contacted status matches: When the contacted status matches the selected options, the users lead count will reduce
- Job status changes to: When the job moves the the stage chosen, their lead count will reduce (paid and payment skipped are treated the same)
- Manual email sent: The lead count can be reduced if the user sends a manual email to the customer
- Call log added: If a call log is added, the lead count can be reduced. The contacted status can be used for a more specific reason for the lead count reducing (e.g. successful contact vs an attempt)
Note: the lead count will only reduce once based on rule that is triggered first. E.g. if a call log is added, this will reduce the users lead count. The job status changing will not reduce their count further.
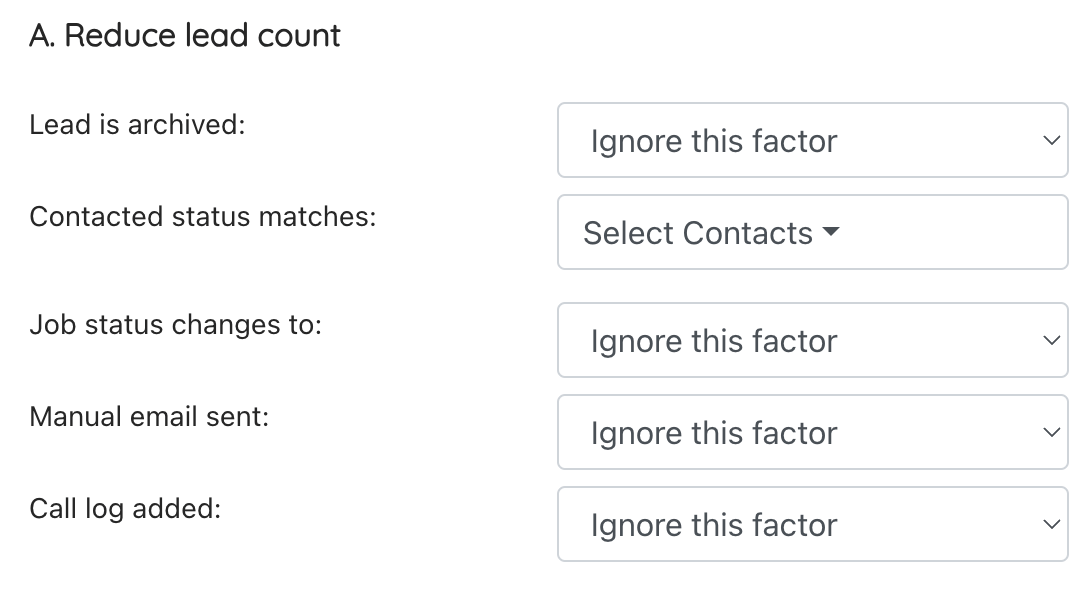
B. Prevents reallocation
The rules below can be used to determine which lead status’ prevents a lead from reallocating to another user:
- Lead is archived: If yes, the lead will not be reallocated to another user
- Contacted status matches: When the contacted status matches the selected options, the lead cannot be reallocated to another user
- Job status changes to: When the job moves the the stage chosen, the lead remains with the current user. This includes stages after the stage chosen automatically (e.g. select “Paid” and if the job is at paid/payment skipped, accepted, booked etc the lead will not reallocate).
- Manual email sent: If a manual email is sent, this would stop the lead being reallocated to another user
- Call log added: If a call log is added, this would prevent the lead from being reallocated to another user. The contacted field can be used for more granular control.
Step 5: Lead reallocation rules
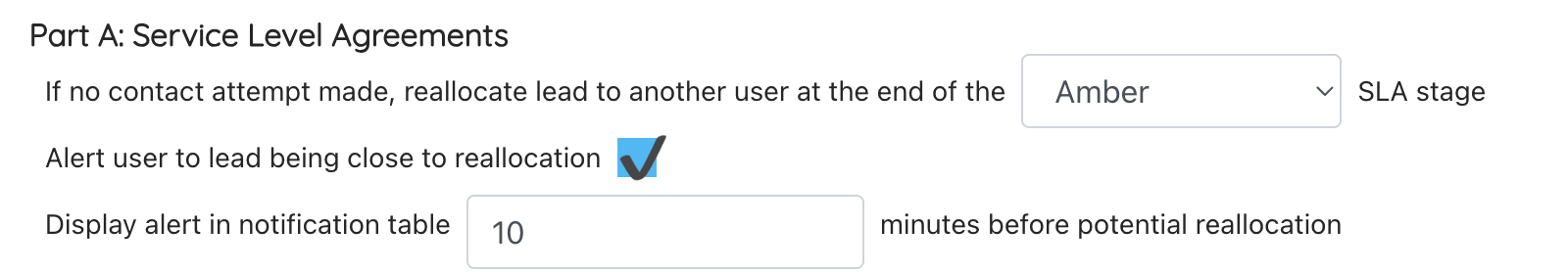
Part A: Service Level Agreements
Set at the end of which SLA stage a lead should be reallocated to another user if the lead doesn’t meet the prevents reallocation settings above.
- Set if the user should be alerted to a lead being close to reallocation
- If so, set how long before reallocation an alert should show in the notifications table (under the SLA tab)
Note: this setting is based on the user’s SLA colour and not the company’s SLA colour. The company SLA times will apply to the user to show how long they’ve had the lead. Once a user gets to the end of the selected colour, the lead will reallocate to someone else. Note: the user SLA will reset when the lead is assigned to the new user to show how long they’ve had the lead.
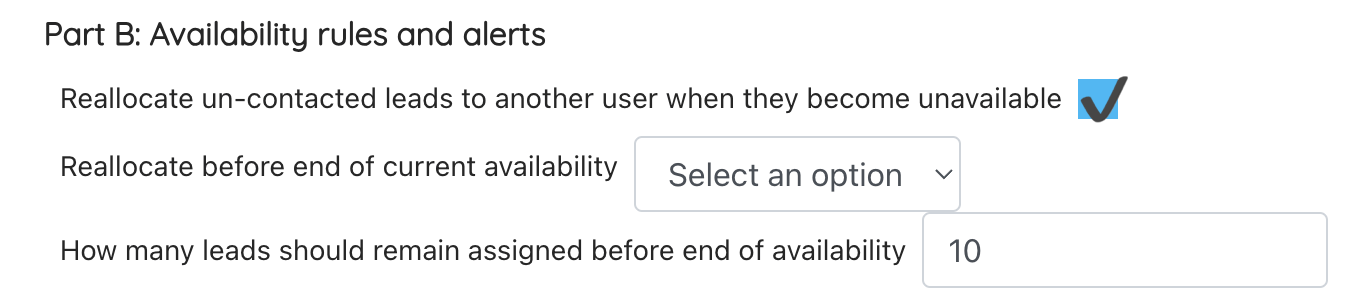
Part B: Availability rules and alerts
Set how leads should be reallocated when a user becomes unavailable:
- Set if leads that do not meet the prevents reallocation rules above should be reallocated to another user when they become unavailable
- Set if leads should be reallocated before a user becomes completely unavailable – choose how soon before
- Select how many leads the user should keep before they become fully unavailable if reallocating leads before the end of their shift
When a user meets these conditions, the leads will be shared amongst the available users that can receive leads in a round-robin or lowest lead count method based on your selection the lead allocation steps.
Part C: Duplicate leads
When a duplicate lead (based on your lead allocation rules above) is allocated to the original user, it will be allocated even if they are unavailable to prevent duplicate contact. However, if this new lead reaches the SLA time and other reallocation factors, the lead will come up for reallocation to be distributed to another user.
When this ‘duplicate’ lead is allocated to another user, we can consider the status of the related leads.
Rule: Reallocate duplicate leads to the new user if another active lead also set to reallocate
If active, this rule prevents a duplicate lead that meets the reallocation rules from being reallocated if the other duplicate lead (or original lead) meets the prevent reallocation rules. I.e. this duplicate will not be reallocated to someone else.
If inactive, this lead will be reallocated to a new user along with any other duplicates that haven’t met the prevent reallocation rules. Any duplicates that do meet the prevent reallocation rules will remain with the current user.

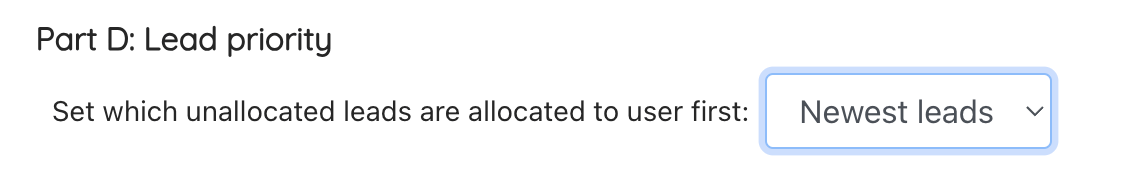
Part D: Lead priority
When users are unavailable for allocation (availability, lead capacity met etc), when users become available, set if the newest leads in the allocation pot or oldest leads in the allocation pot should be prioritised first.
Step 6: Lead age
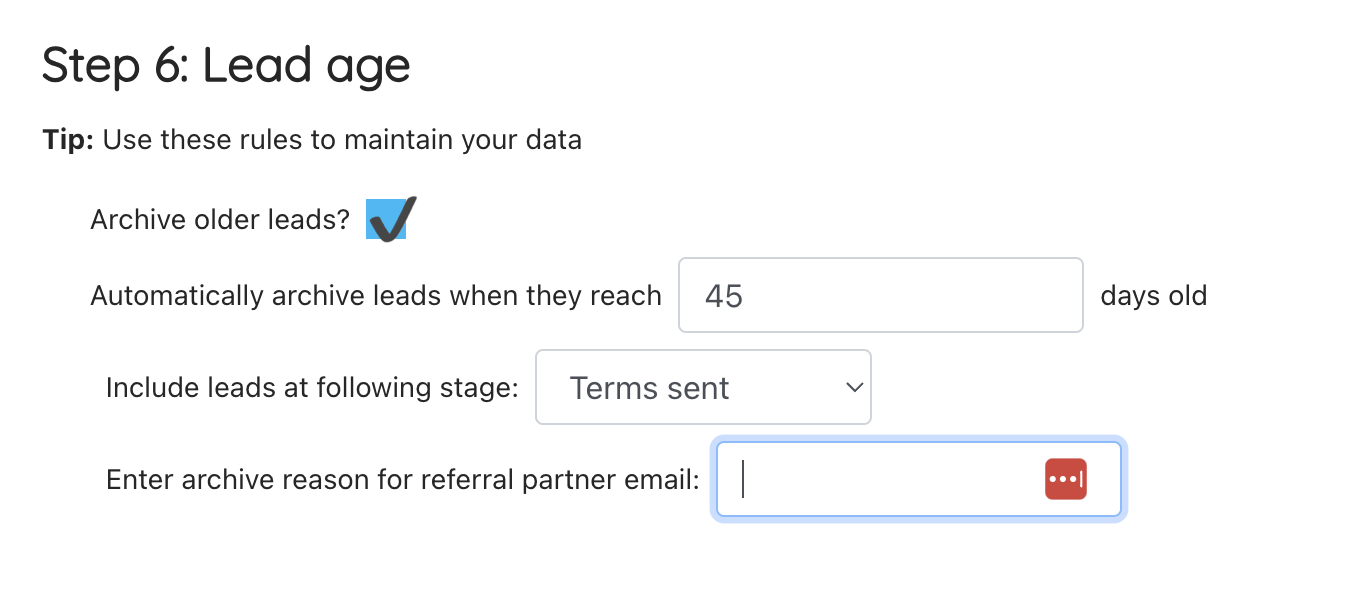
Archiving leads
Set if older leads should be archived or not:
- Set the age at which they should be archived
- Set which lead stages should be included
- Set a standard reason to include in your referral partner templates (if using the lead archived template)
These rules can help you automatically clear down leads that haven’t converted.
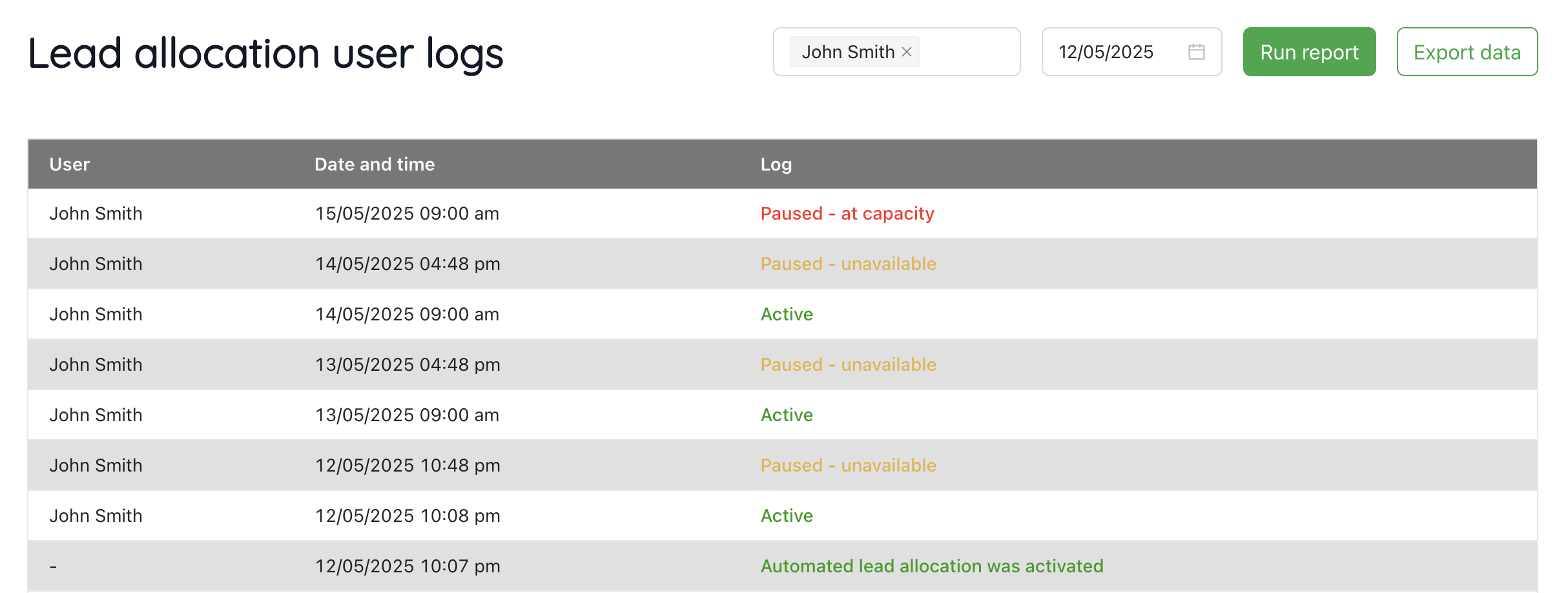
User allocation logs
You can use the user allocation logs under Settings > Manage users > Lead allocation user logs in order to see when a user was available for leads or unable to receive leads.
Open the page, select a user and a date and press “Run report”.
The page will show all logs from the selected date onwards.
FAQs
If I mark a duplicate lead as not a duplicate how does this affect lead count?
When a duplicate lead is allocated to a user, it does not increase their lead account. If a lead is marked as not a duplicate, their lead count will increase (until it meets the reduced lead count rules). This can cause a user to go above their lead capacity limit.
If manually reallocating leads, can I go over a user’s lead capacity?
Yes, the user’s lead count will show higher than their capacity limit if you manually reallocate leads to a user and they are already at capacity.
What happens to job tasks when a lead is reallocated?
Any active tasks will be reallocated to the new user too (ignoring tasks that are marked cancelled or completed). This is the same if the job is automatically reallocated or manually reallocated (via the reallocate button on the quotes table).
What do the two SLA bars show?
The first bar shows the overall company SLA. The second bar shows how long the allocated user has had the lead allocated to them.
What happens to lead counts if a lead is deleted?
The lead count will be reduced by 1, provided that the lead count hasn’t already been reduced by a job factor that reduces the lead count.
How is the lead allocation/reallocation process managed?
When new leads come in, they are allocated immediately.
The lead allocation/reallocation process also runs every 5 minutes so that if users have started and there is a queue of leads they can be allocated to someone.
What happens if I turn lead allocation off and back on?
When turning off lead allocation via the activation slider at the top of the page, this stops lead allocation and reallocation from running. When turned back on, only leads added after the lead allocation process was turned back on will be allocated and reallocated. Older leads from before this will not be included in the automated process. This is to prevent issues with historical leads being reallocated/allocated.
If you want to pause allocation so that when it is active again it includes leads since you first turned on lead allocation, you can set all users to unavailable. This will prevent any leads being allocated/reallocated in this time (other than duplicate leads).
Leads are set to reallocate but they are still assigned to the first user
If there are no “available” users (users who meet the criteria in your settings), the leads will remain assigned to the first user until other users become available. This ensures the leads can still be worked via the first user until others are available instead of the leads sitting unallocated and untouched by any user.
SLAs
If you have ticked a user cannot receive new leads if they have leads at an unticked SLA stage (e.g. Red), if the user has any leads that are at that stage, this will still apply even if the lead is archived to prevent gaming. The user must complete their SLAs before archiving.

